SGPA and CGPA: Definition, How to Calculate, Difference
Students who want to follow their academic progress must effectively understand the academic metrics of SGPA (Semester Grade Point Average) and CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average). The metric to evaluate student semester-level performance is SGPA. Each student earns points by multiplying grades with credit hours, followed by a total credit-hour division that attributes the final points’ values. This mathematical calculation reflects a student’s performance in one program period.
CGPA represents a summarization of academic results across different semesters which combines all semester performance evaluations throughout student attendance at educational programs. The total grade points earned across each semester turn into CGPA when divided by the total number of credit hours attempted. The key difference lies in their focus: SGPA shows a single semester evaluation yet CGPA shows continuous academic performance from which students determine educational trajectories leading to prospects. Students need a full comprehension of SGPA and CGPA to establish substantial academic targets and make important educational choices.
What is SGPA (Semester Grade Point Average)?
Through SGPA educational institutions assess student academic performance in a specific period of one semester by evaluating total grade points against total credit hour requirements. The SGPA computation involves dividing total grade points from taken courses by the combined credit hour total of those courses over a semester. Educational institutions assign credit levels to courses as students convert their grades into points on a rating scale of 0 to 4 or 0 to 10 according to institutional grading policies. Students gain insights about their performance skills and weaknesses through SGPA which delivers immediate evaluation of their semester work. A strong SGPA determines the student’s position within their academic program and eligibility for different scholarship opportunities or dignified recognition. Regular examination of SGPA enables students to develop education-oriented goals and make knowledgeable decisions about their educational progression.
A student’s SGPA results from grading their courses with appropriate grade points. Students obtain grade points by deducting credit hours from grade point values belonging to their letter grades. The credit points total divided by the total attempted credits determines the computed SGPA.
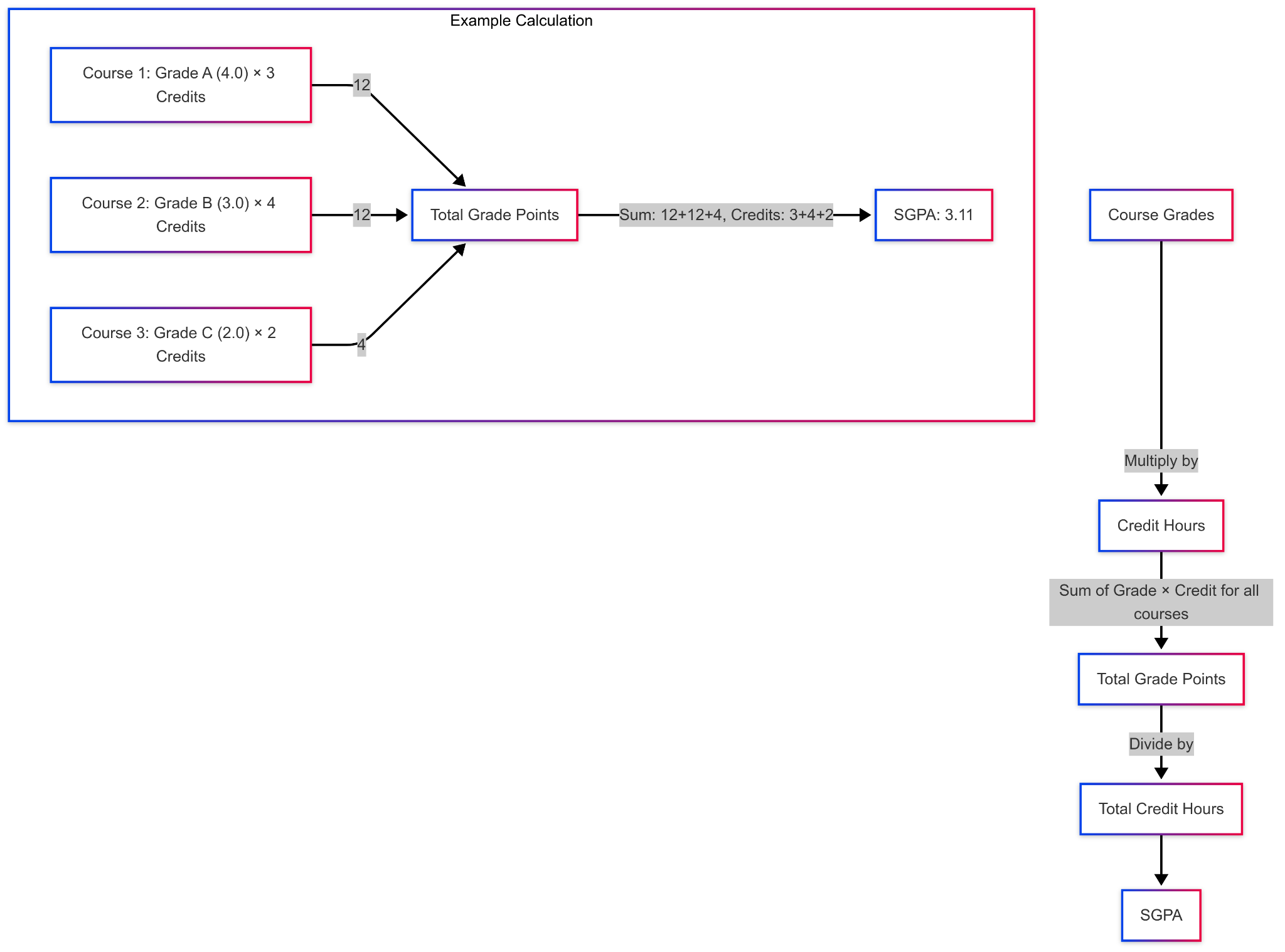
For Example:
- Students who earn an ‘A’ in 3 credit hour classes will receive a course grade point of 12 by multiplying 4.0 by 3.
- Students who get a ‘B’ in a two-credit course earn 6-course grade points because 3.0 grade points are multiplied by 2 credits.
- A four-credit hour course earns ‘A’ students a grade point value of 4.0 which adds up to a total of 16 points (4.0 multiplied by 4 credits).
- Teachers who earn a ‘C’ in a single credit hour course receive a 2.0 grade point value that translates to a total of 2 points (2.0 x 1).
Added together these grades yield 36 GPA points from 10 attempted credit hours (3+2+4+1). The semester SGPA is calculated as 3.6 because 36-grade points are divided by 10 credit hours.
What exactly is CGPA & how is CGPA calculated?
In higher educational institutions Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) provides the standardized means to evaluate student academic achievements across multiple subjects. The system allows students to obtain a holistic view of subject performance throughout predefined academic timeframes that extend to semesters or full academic years. CGPA functions better than percentage grades because it creates standardized subject score measurements which enables straightforward assessment of academic metrics.
The calculation of CGPA typically involves three main components: A student’s performance calculates Universities determine the credit value for each course through a combination of learning challenge and duration requirements. Student grades produce grade point values through which ‘A’ standing earns 4 points while ‘B’ earns 3 points along with additional points for different grade levels. Students obtain their CGPA score by dividing their cumulative grade points from all subjects with their total credit hours.
For Example
Students collect their cumulative grade point average (CGPA) by dividing the total earned grade points from all semesters by the total earned credits throughout the course duration. The formula for CGPA is:
- The cumulative grade point average is computed by dividing total grade points from every semester by the total number of credits registered during all semesters.
- The grade points earned by students in each semester should be added together to get a total value. A student earns points by multiplying their assigned grade points with the number of completed credits for every class they take.
- One student receives 27-grade points from their ‘A’ grade in a three-credit course because 9-grade points match ‘A’ score points multiplied by the 3 credits.
- The total grade point total for all semesters becomes known by combining all the grade points earned during each academic period. To calculate the final result you must total all course credits regardless of the semester.
- To calculate the CGPA simply divide the total grade points earned by total accumulated credits across the entire period of study. The acclaimed student number signifies their CGPA result.
How is CGPA different from SGPA?

Management institutions utilize two fundamental grading systems namely CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) and SGPA (Semester Grade Point Average) to evaluate student academic success. Their functions remain distinct from one another. A student’s semester performance transforms into SGPA by averaging their grades from all their semester courses before it reaches its completion. Students can view their academic progress through an instant snapshot across their selected courses throughout the semester.
The aggregation of every SGPA score recorded in a program results in the CGPA calculation which demonstrates the student’s combined learning achievements throughout extended training periods. Significant Grading Points Average offers immediate score information yet Cumulative grade point average presents an inclusive evaluation of performance across multiple semesters between beginning and ending a course or degree program.
How do you convert a CGPA to a percentage?
Students can determine their academic performance through CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) which consists of averaging their obtained grade points from all semesters. To convert CGPA to percentage, use the formula:
Percentage = CGPA × 9.5.
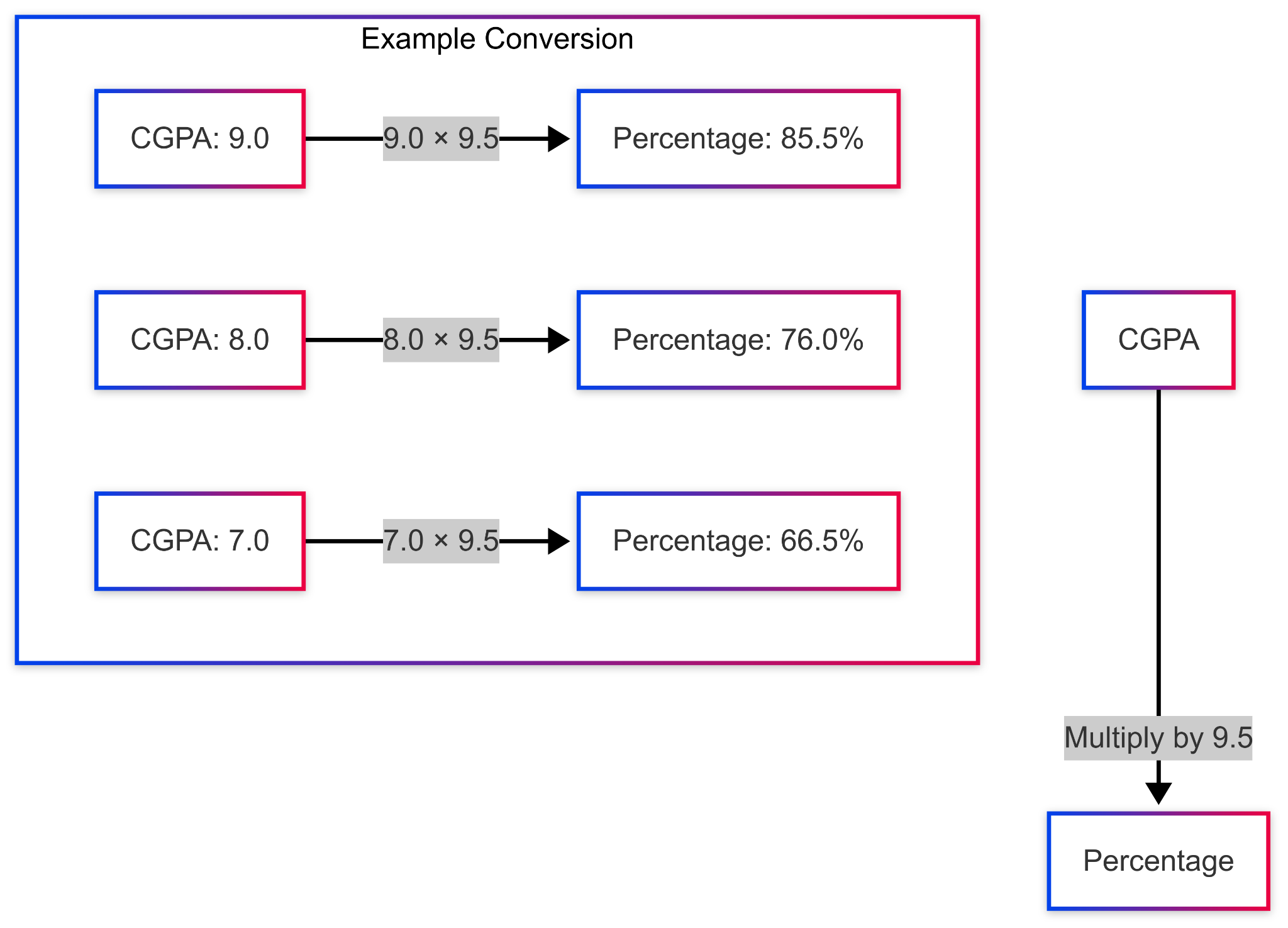
CGPA to Percentage Calculator
The grading system has a fixed ratio which establishes a 100% match between a maximum GPA rating of 10 and a standard scale of 100 points. For instance, a CGPA of 8.2 converts to 77.9% (8.2 × 9.5 = 77.9%). Schools operate different conversion procedures which students must verify through official guidelines.
How do you convert SGPA as a percentage?
Students calculate semester grade points average (SGPA) by dividing total earned grade points by total registered credit hours. Then, use this formula to convert SGPA to a percentage:
Percentage = SGPA x Maximum Grade Point x IO.
Each academic institution establishes its maximum grade points yet a 10-point system prevails as the standard in Indian educational systems. Therefore, the SGPA percentage calculation in India is:
Obtain the Semester Grade Point Average by dividing Overall Grade Points by Total Credit Hours.
Percentage = SGPA x IO x 100.
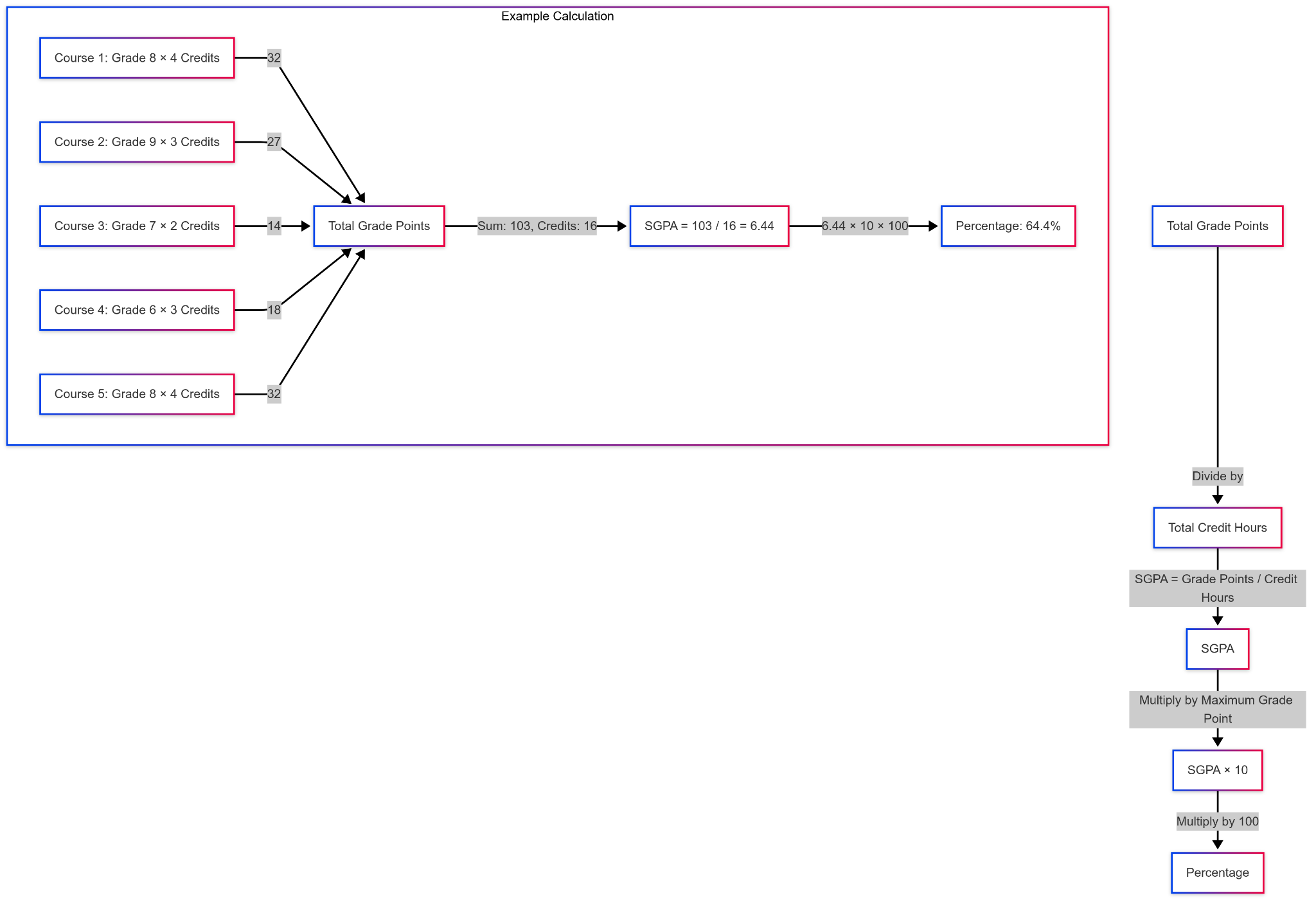
For example: One student enrolled in five courses while earning final grades of 8, 9, 7, 6, and 8 which totaled 103 grade points.
– Total grade points: (8×4) + (9×3) + (7×2) + (6×3) + (8×4) = 103.
– Total credit hours: 4 + 3 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 16.
Thus, the SGPA is calculated as:
SGPA = 103 / 16 = 6.44 (rounded).
To convert SGPA to percentage:
Percentage = 6.44 x 10 x 100 = 64.4%.
So, the student’s SGPA of 6.44 equals 64.4%. The conversion processes differ among institutions so students need to confirm the official guideline procedures.
Grading system
Standardized grading systems represent the framework through which teachers evaluate their students’ understanding and performance in educational institutions. Collapsable grading systems rely on letters across A B C D and F ranges together with numbers for student work quality. Implementing this assessment approach enables faculty members to evaluate academic success but it simultaneously supplies students with specific metrics for learning health monitoring.
While grading systems can vary between schools and educational institutions, their primary goal remains the same: This system maintains dual purposes for student motivation as well as educational direction.
Here’s a table summarizing the grading system commonly used in Indian educational institutions:
Grade | Percentage Range | Grade Point (GPA/CGPA) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
A+ | 90% – 100% | 9.0 – 10.0 | Outstanding |
A | 80% – 89% | 8.0 – 8.9 | Excellent |
B+ | 70% – 79% | 7.0 – 7.9 | Very Good |
B | 60% – 69% | 6.0 – 6.9 | Good |
C+ | 50% – 59% | 5.0 – 5.9 | Average |
C | 40% – 49% | 4.0 – 4.9 | Below Average |
F | Below 40% | Below 4.0 | Fail |
Conclusion
The student evaluation process relies fundamentally on SGPA together with CGPA to help students monitor their academic progression. Students gain performance insights from SGPA which lets them make planned strategy improvements for better academic outcomes. The CGPA methodology sums up student academic results spanning their entire college career to present an expanded summary of student accomplishments. Proper comprehension of these academic measures with their specific calculations forms a foundation for strategic academic planning which helps students create practical educational targets and select appropriate choices. Students who track both SGPA and CGPA periodically find it easier to handle their academic path progress and exploit future possibilities.
FAQs
1. What is SGPA?
A: SGPA represents a system to measure students’ cumulative academic achievement during their selected semester.
2. How do you calculate SGPA?
A: For calculating your Semester Grade Point Average you must multiply your grade points by their course credits. Afterward, you need to divide this total by all your attempted course credits during that semester.
3. Why do SGPA and CGPA differ from each other?
A: Students receive their semester performance information through SGPA (Semester Grade Point Average) while CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) shows the cumulative performance over an entire educational program.
4. How can I convert my CGPA to a percentage?
A: You can calculate your course percentage by multiplying your CGPA by 9.5. The CGPA of 8.2 when converted uses a formula of (8.2 × 9.5 = 77.9% to obtain a 77.9% percentage. Before proceeding check with your institution because their methods of conversion might differ.
5. What standard grading system operates across India?
A: Standard grading at Indian educational institutions operates using a system of grades between A+ down to F which matches particular percentage zones and value points.